Joule Collection
Joule, the unit of energy named after James Prescott Joule, an English physicist who made significant contributions to the field of thermodynamics in the 19th century
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
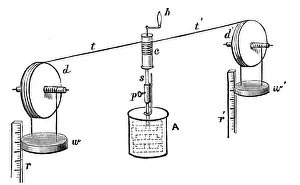
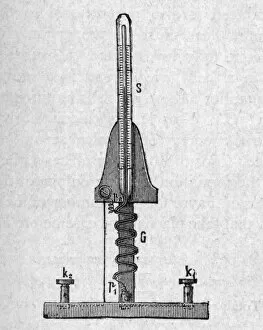
Joule, the unit of energy named after James Prescott Joule, an English physicist who made significant contributions to the field of thermodynamics in the 19th century. Born in 1818 and passing away in 1889, Joule's work revolutionized our understanding of electricity and heat. One of his most notable achievements was determining the mechanical equivalent of heat through his apparatus. This groundbreaking invention allowed for precise measurements that established a relationship between mechanical work and thermal energy. In various portraits captured throughout his lifetime, we see a man dedicated to unraveling the mysteries surrounding energy. From oil on canvas by George Patten to pen and ink drawings from the 20th century, these images depict a brilliant mind at work. Joule's experiments paved the way for advancements in electrical power generation and distribution systems that we rely on today. His discoveries laid a foundation for modern physics and engineering principles. The joule is now widely used as a standard unit to measure energy across different fields such as mechanics, electronics, and even nutrition. It represents both potential and kinetic forms of energy present in everyday life. As we continue to harness electricity's power for technological progress, let us remember James Prescott Joule - an innovator whose legacy lives on through this fundamental unit of measurement bearing his name.