Infarction Collection
Infarction, commonly known as a stroke, is a serious medical condition that can have devastating effects on the body
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
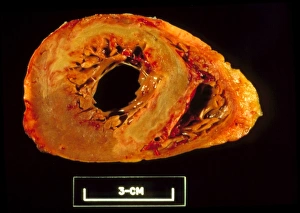
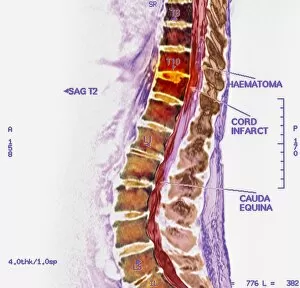
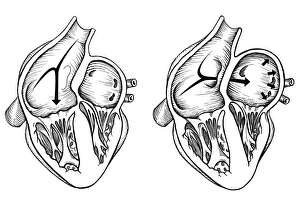
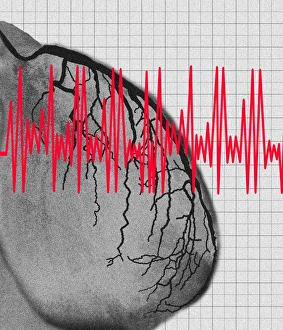
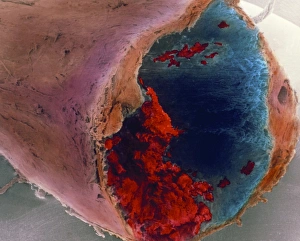
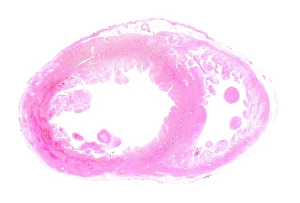
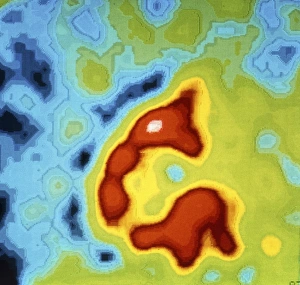
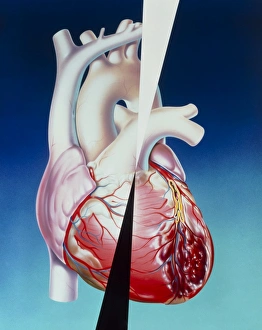
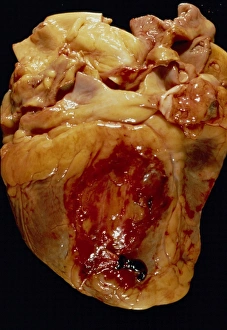
Infarction, commonly known as a stroke, is a serious medical condition that can have devastating effects on the body. Advanced imaging techniques such as MRI and 3D CT scans (C016 / 6419) play a crucial role in diagnosing and understanding this condition. One specific type is splenic infarct (C015 / 6220), which occurs when blood flow to the spleen is blocked, leading to tissue damage. This condition can also be visualized using MRI scans. Another form that affects the spinal cord can be detected through an MRI scan. Spinal cord strokes are rare but require immediate medical attention due to their potential for long-term disability. Comparing normal hearts with those having a patent foramen ovale reveals significant differences. A patent foramen ovale refers to an opening between two heart chambers that should normally close after birth but remains open in some individuals. This condition increases the risk of stroke by allowing blood clots or other materials to travel from one side of the heart to another. In some cases, ventricular wall rupture may occur following an infarction, resulting in life-threatening complications. Medical illustrations help visualize this phenomenon and aid in understanding its impact on cardiac health. Artwork depicting a tablet computer alongside heart attack imagery (F006 / 4625) highlights how technology plays a vital role in educating people about cardiovascular diseases like infarctions. MRI and 3D CT scans are not limited to studying brain-related conditions; they are also used extensively for examining various parts of the human body including the head (LM of section whole heart showing LV infarct). These images provide valuable insights into different types of infarctions affecting diverse organs such as splenic infarcts (C015 / 6221 & C015 / 6219). Heart angiograms and ECGs serve as essential diagnostic tools for identifying heart attacks.