High Energy Collection
"Unleashing the Power of High Energy: Exploring the Mysteries of the Universe at CERN" Step into the world physics
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
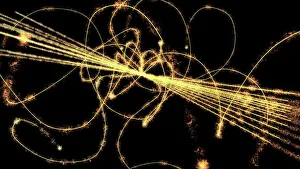
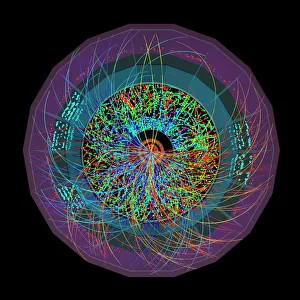
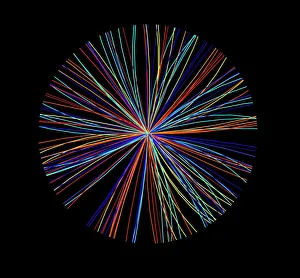
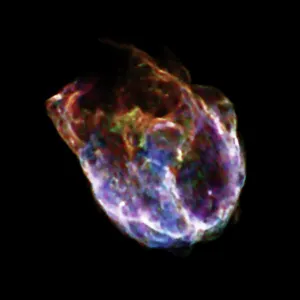
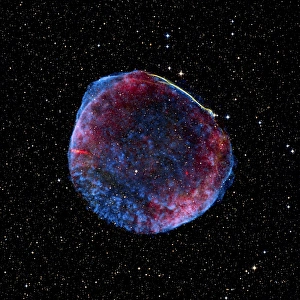
"Unleashing the Power of High Energy: Exploring the Mysteries of the Universe at CERN" Step into the world physics, where groundbreaking experiments and mind-boggling collisions take place. At CERN, home to cutting-edge scientific research, two remarkable detectors stand tall - ATLAS and CMS. These colossal machines are at the forefront of unraveling the secrets hidden within particles. In this captivating artwork, a particle physics experiment comes alive as vibrant colors dance across the canvas. It symbolizes our relentless pursuit to understand nature's building blocks and their intricate interactions. Witness an extraordinary phenomenon - lead ion collisions. As these tiny particles collide with tremendous force in accelerators like LHC, they create conditions akin to those moments after the Big Bang. Scientists delve into this cosmic chaos to unlock fundamental truths about our universe's origins. Gaze upon Zeta Ophiuchi bow shock captured through an infrared lens - a mesmerizing display of energy unleashed by a massive star hurtling through space. This celestial spectacle reminds us that high energy phenomena exist not only on Earth but also throughout our vast cosmos. Behold Supernova remnant N132D in its X-ray glory. The remnants left behind by exploding stars emit intense radiation, providing invaluable insights into stellar evolution and cataclysmic events that shape galaxies. Venture deep underground into the labyrinthine tunnels housing LHC - a technological marvel spanning kilometers beneath CERN's surface. Within these tunnels lies humanity's quest for knowledge; where scientists push boundaries using unimaginable energies to explore uncharted territories. Marvel at galaxy cluster collision imprinted in X-ray brilliance. Witnessing such immense forces colliding is like witnessing nature's grandest fireworks display – illuminating dark matter mysteries while shaping galactic landscapes. High energy science takes us beyond what we can see with naked eyes; it propels us towards understanding existence itself.