Haemorrhage Collection
"Unveiling the Silent Menace: Exploring the World of Haemorrhage" Delving into the microscopic realm
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
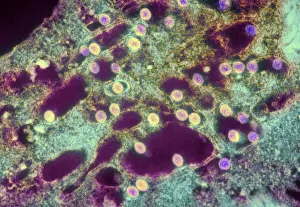
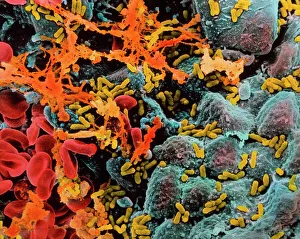
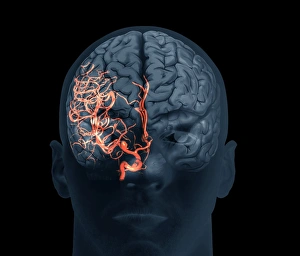
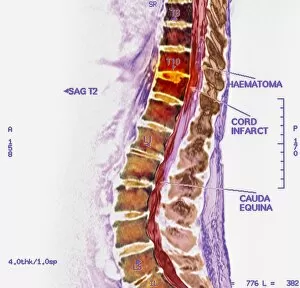
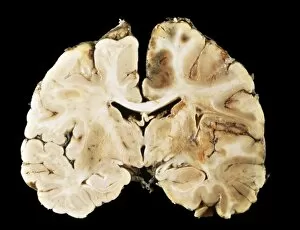
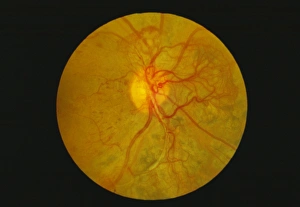
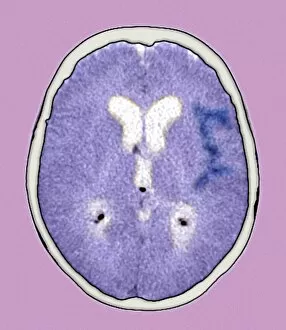
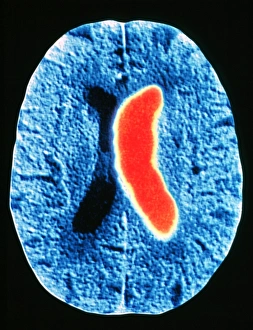
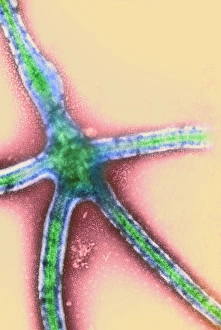
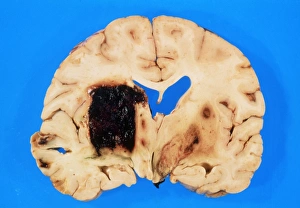
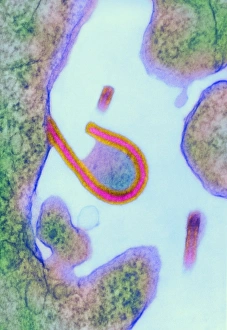
"Unveiling the Silent Menace: Exploring the World of Haemorrhage" Delving into the microscopic realm, Rift Valley fever virus particles are captured in stunning detail through TEM, revealing their potential to cause haemorrhagic fevers. Bladder infection takes an unexpected turn as haemorrhage becomes a distressing symptom, highlighting the severity and complications associated with this common ailment. The intricate beauty of Dengue fever virus particles is unveiled under TEM, shedding light on how these tiny entities can trigger severe bleeding disorders in infected individuals. Unraveling history's mysteries, we revisit "The Death of Felix Faure" from Le Petit Journal—a captivating depiction that raises questions about the role in his untimely demise. An intriguing page of advertisements engraved with precision showcases medical advancements aimed at preventing and treating various forms of haemorrhage—reflecting society's ongoing battle against this formidable foe. Peering into medical imaging technology, a 3D scan reveals a brain aneurysm—an alarming reminder that silent ruptures within our delicate cerebral vessels can lead to life-threatening haemorrhages. A haunting image captures Brain Injury C016/8920—a stark reminder that traumatic events can result in devastating internal bleeding and emphasising the urgent need for improved prevention strategies. Through cutting-edge MRI scans, we witness the aftermath of spinal cord stroke—a rare but catastrophic event causing paralysis due to sudden blood vessel rupture within our vital neural pathways. Cross-sectional biomedical illustrations vividly portray complete placenta praevia—an obstetric complication where abnormal positioning leads to dangerous maternal haemorrhaging during childbirth—underscoring its critical nature for expectant mothers worldwide. Revealing another perilous condition affecting pregnancy, biomedical art exposes placental abruption—a potentially fatal occurrence where detachment triggers massive bleeding, demanding immediate medical attention.