Glial Cell Collection
Glial cells, also known as neuroglia or glia, play a crucial role in the intricate workings of our nervous system
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
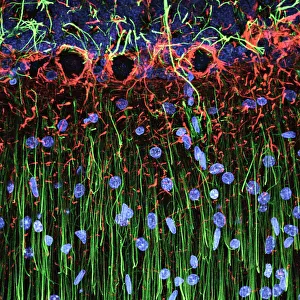
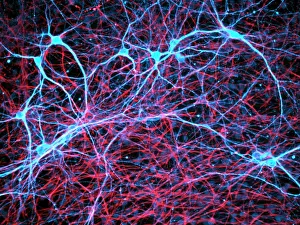
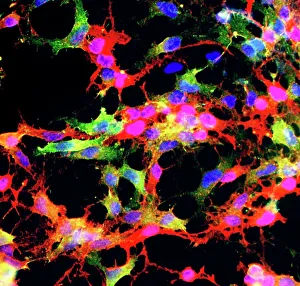
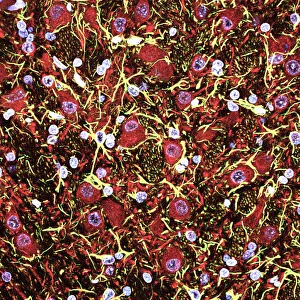
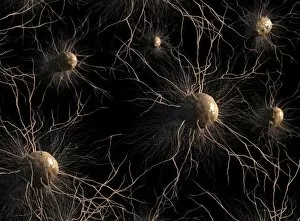
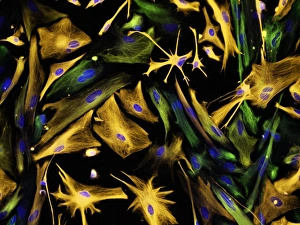
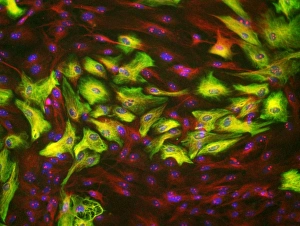
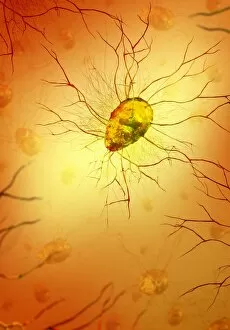
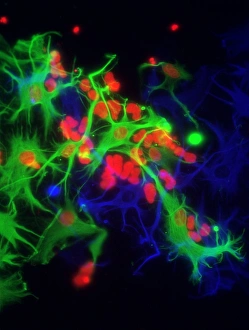
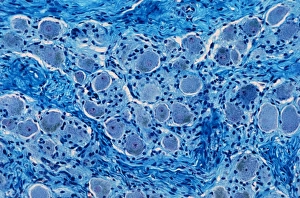
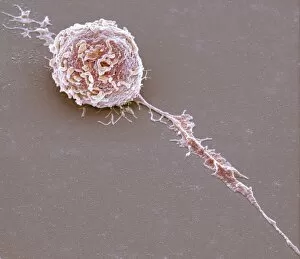
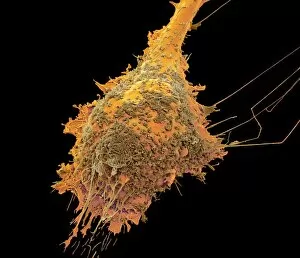
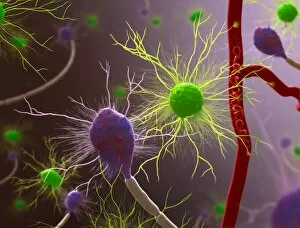
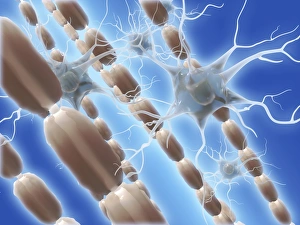
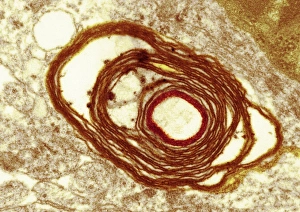
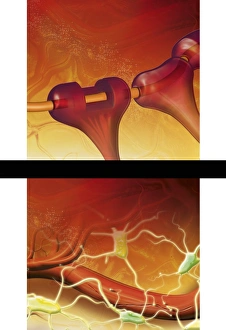
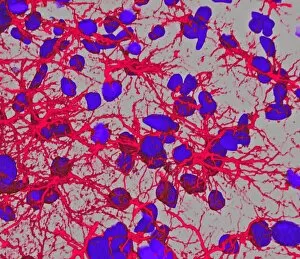
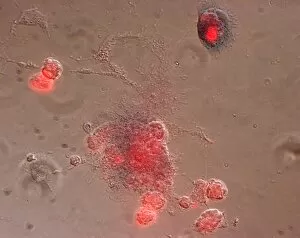
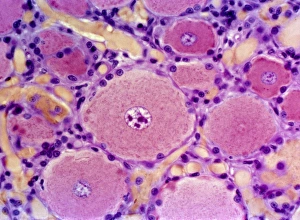
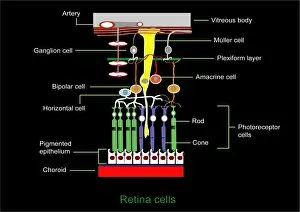
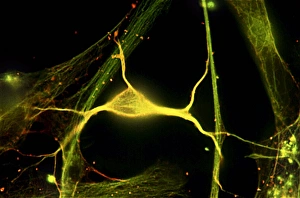
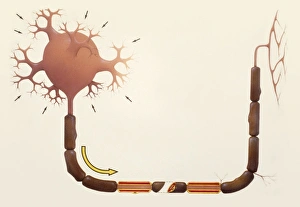
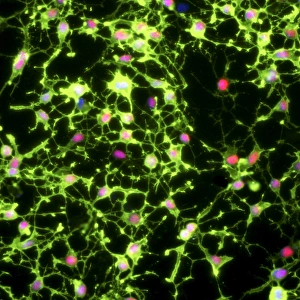
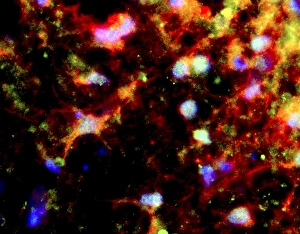
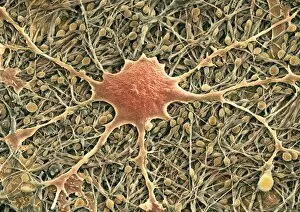
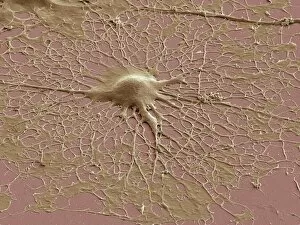
Glial cells, also known as neuroglia or glia, play a crucial role in the intricate workings of our nervous system. These unsung heroes provide support and protection to nerve cells, ensuring that our brain functions smoothly. In cerebellum tissue, when observed under a light micrograph, one can see the delicate network of glial cells intertwined with nerve cells. Their presence is vital for maintaining the structural integrity of this region responsible for motor coordination and balance. Another fascinating glimpse into their world can be seen through a light micrograph showcasing both nerve and glial cells. Here, we witness their close proximity and symbiotic relationship within neural tissue. Glial cells not only nourish neurons but also regulate neurotransmitter levels, aiding in efficient communication between these essential building blocks of our nervous system. Confocal light micrographs reveal an enchanting view of glial cells alone. These images capture their intricate morphology as they extend their processes to interact with neighboring neurons. This interaction is critical for neuronal survival and synaptic plasticity. In stem cell cultures derived from neural progenitors, we witness the remarkable ability of glial stem cells to differentiate into various specialized types such as astrocytes – star-shaped glial cells found throughout the cerebral cortex. Artwork depicting astrocyte nerve cells showcases their unique structure and highlights their importance in maintaining brain homeostasis. Myelin sheaths are another key feature associated with glial cells' function. Artwork portraying myelin sheaths alongside glial cell structures demonstrates how these supportive elements wrap around axons like protective insulation – enabling faster transmission of electrical signals along nerves. Light micrographs further emphasize the significance of astrocyte brain cells by capturing them individually or in clusters within different regions of the central nervous system (CNS). Their diverse roles include regulating blood flow to meet neuronal demands and providing metabolic support to ensure optimal brain functioning. Lastly, stem cell-derived astrocyte brain cells offer a glimpse into the future of regenerative medicine.