Geo Centric Collection
"Exploring the Geo Centric Universe: Tracing the Evolution of Astronomical Beliefs" Step into the world of ancient astronomy as Urania, the Muse of Astronomy
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
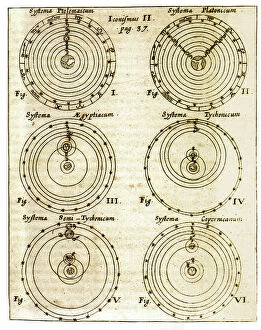
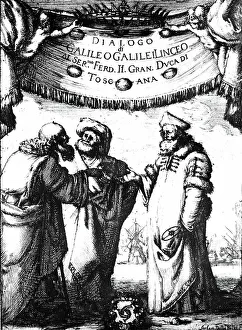
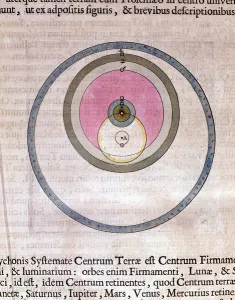
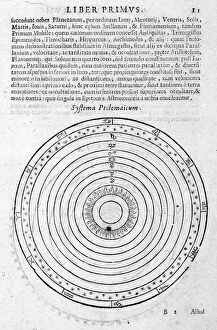
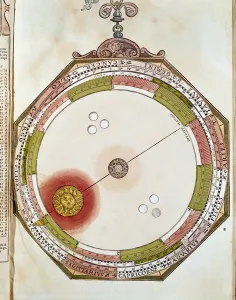
"Exploring the Geo Centric Universe: Tracing the Evolution of Astronomical Beliefs" Step into the world of ancient astronomy as Urania, the Muse of Astronomy, stands proudly in front of Argus, clutching a telescope. This captivating image takes us back to a time when our understanding of the cosmos was vastly different. In 1482, Ptolemy's map was published, showcasing his intricate knowledge and calculations. Claude Ptolemy himself, a revered Greek scholar and astronomer from centuries past, is immortalized in an engraving titled "Canon Astronomicon, " symbolizing his immense contribution to celestial studies. Fast forward to 1632 when Galileo Galilei shook the foundations with his groundbreaking work. The frontispiece to his book "Dialogo sopra i due massimi sistemi del mondo" depicts him surrounded by engravings that capture both awe and controversy, and is here that we witness Galileo challenging traditional beliefs with undeniable evidence. Delve deeper into this era through another engraving from Galileo's book cover titled "Dialogo di Galileo Galilei Linceo Al Sermo. Ferd. II. Big Duca di Toscana. " These engravings transport us back to a time where intellectual curiosity clashed with societal norms. An armillary sphere from the 17th century further emphasizes humanity's quest for understanding celestial bodies. Its intricate design serves as a testament to our relentless pursuit of knowledge about our place in the universe. The Middle Ages come alive through an illuminure depicting Aristotle as a teacher—a reminder that even during times marked by limited scientific progress, there were still those who sought wisdom beyond conventional boundaries. Lastly, we encounter two significant works: Ptolemy's system of the world showcased in "Harmonia Macrocosmica" and an enchanting sun illustration found within "Astronomicum Caesarium.