Gaffurius Collection
Franchinus Gaffurius (1451-1522) was an influential Italian music theorist and composer
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
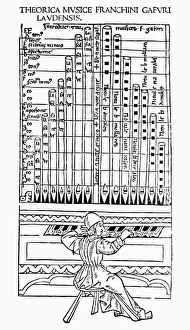
Franchinus Gaffurius (1451-1522) was an influential Italian music theorist and composer, known for his significant contributions to the field of music during the Renaissance. His works encompassed a wide range of topics, from practical guides on musical performance to theoretical treatises on harmony and instruments. Gaffurius drew inspiration from ancient philosophers like Pythagoras of Samos (570 BC-495 BC), whose ideas about the mathematical relationships in music greatly influenced his work. In fact, Gaffurius's engravings often depicted scenes related to Pythagorean concepts, such as Apollo presiding over the Music of the Spheres or Pythagoras playing musical scales on bells and water glasses. One of Gaffurius's most renowned publications is "Practica Musicae, " which provided detailed instructions for church choirs. This illustrated guide not only served as a valuable resource for musicians but also showcased Gaffurius's artistic talent through intricate illustrations that brought his teachings to life. In addition to "Practica Musicae, " Gaffurius authored other notable works like "Theorica musicae" and "De harmonia musicorum instrumentorum opus. " These texts delved into complex theories surrounding musical scales, harmonies, and instruments. Through woodcuts featured in these books, such as those depicting pipers or organs, Gaffurius aimed to enhance readers' understanding by visually representing various aspects of music-making. Gaffurius's contributions were highly regarded during his time and continue to be studied today. His dedication to both theory and practice solidified him as a prominent figure in Renaissance music history. From engraving scenes inspired by ancient philosophers like Pythagoras to providing comprehensive guides for musicians, Franchinus Gaffurius left an indelible mark on the world of music with his innovative ideas and artistic expressions.