Fibrin Collection
"Fibrin: The Essential Protein in Blood Clotting" In the intricate realm of blood coagulation cascade, one protein stands out as a crucial player - fibrin
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
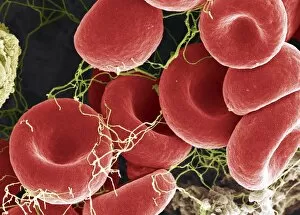
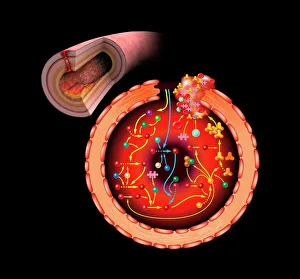
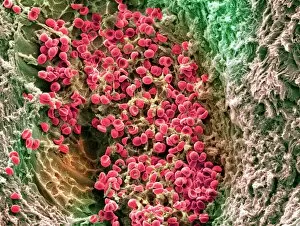
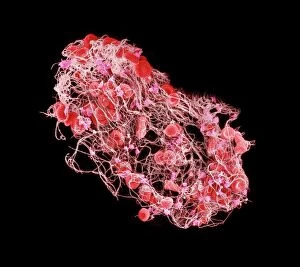
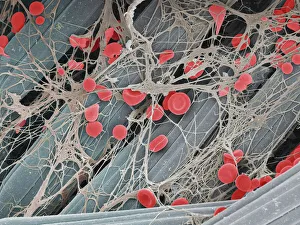
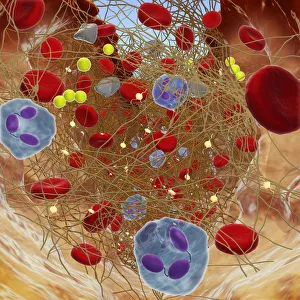
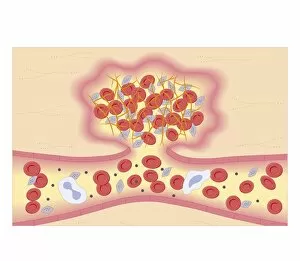
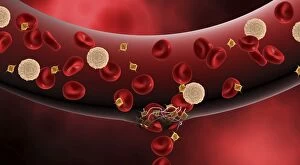
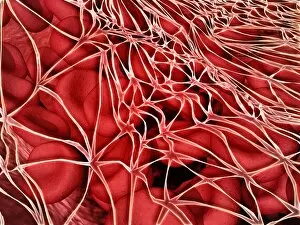
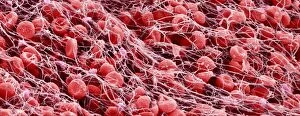
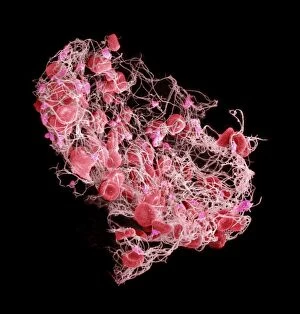
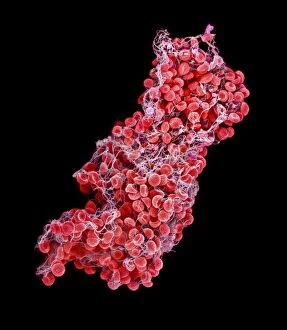
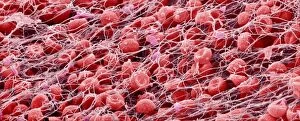
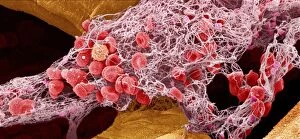
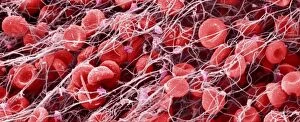
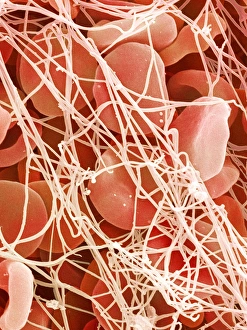
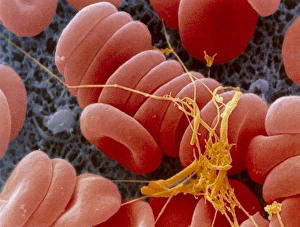
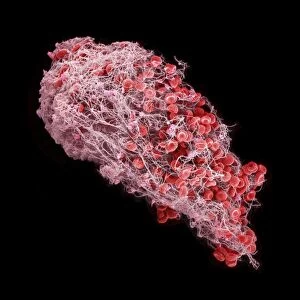
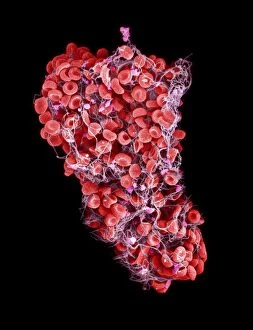
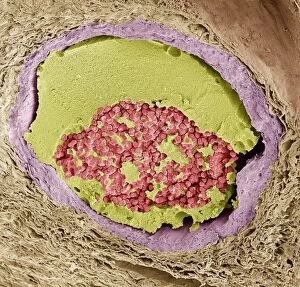
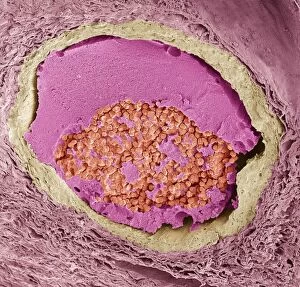
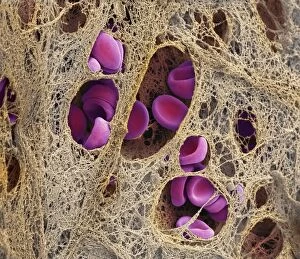
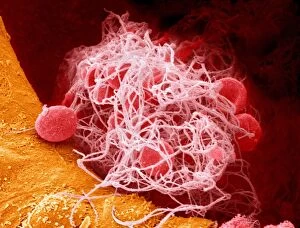
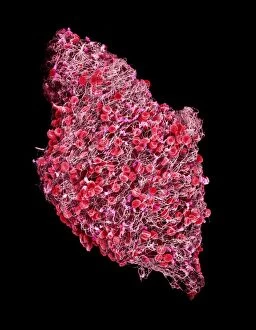
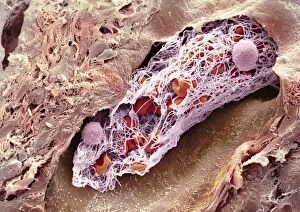
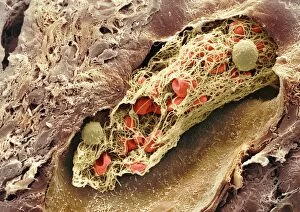
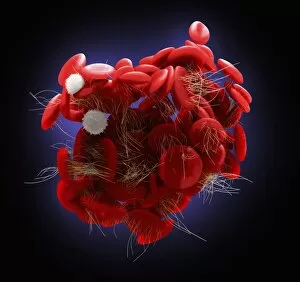
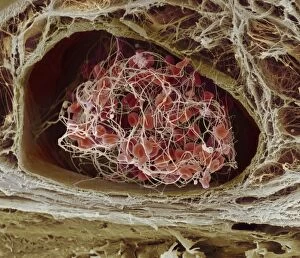
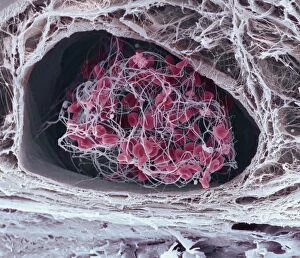
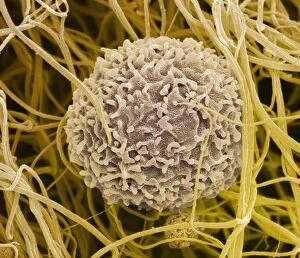
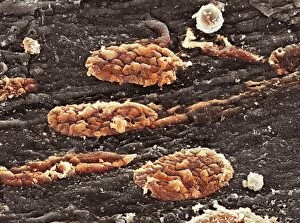
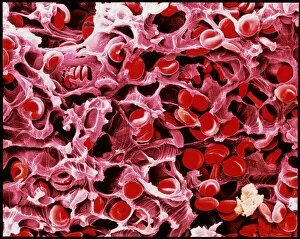
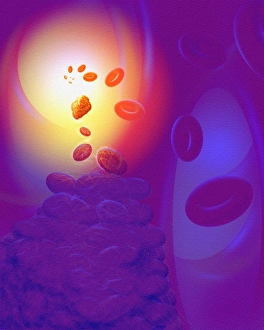
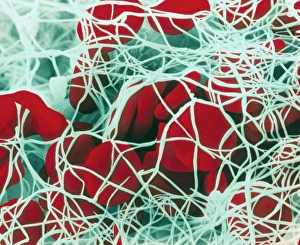
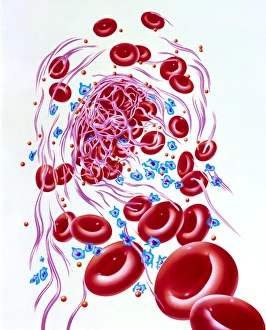
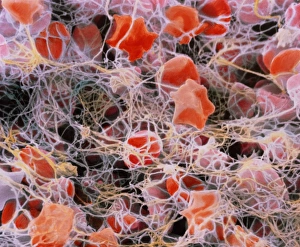
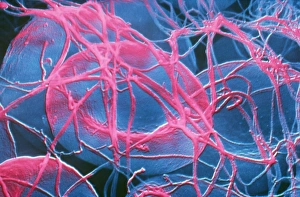
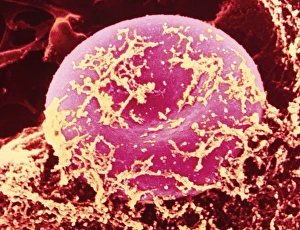
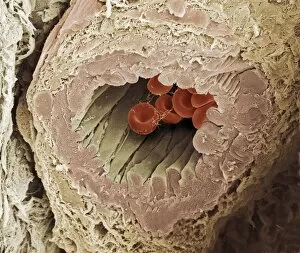
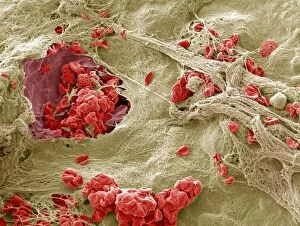
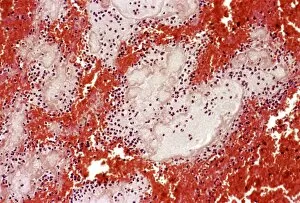
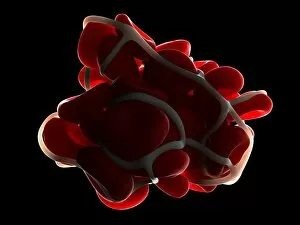
"Fibrin: The Essential Protein in Blood Clotting" In the intricate realm of blood coagulation cascade, one protein stands out as a crucial player - fibrin. Represented beautifully in artwork C016/9873, this captivating molecule takes center stage in the world of Anatomy and Biology. Fibrin's significance lies within its ability to form blood clots, ensuring our bodies can heal wounds efficiently. SEM images such as C016/9747 and those depicting blood clots on plaster showcase the intricate web-like structure that fibrin forms during clot formation. The cross-section biomedical illustration reveals how fibrogen transforms into insoluble fibrin strands, effectively trapping red blood cells and yellow platelets at the site of injury. This visual representation highlights the vital role played by fibrin in preventing excessive bleeding. A closer look at a blood vessel with platelets, white blood cells, and red blood cells emphasizes how these elements work together harmoniously under fibrin's guidance to maintain our health. Conceptual images featuring red blood cells intertwined with fibrin further emphasize this symbiotic relationship. SEM images like C016/9751 and C016/9746 offer an up-close view of intricately formed clots, showcasing the complexity behind their creation. These visuals serve as a reminder of how essential fibrin is for our well-being. So next time you think about clotting or wound healing, remember that behind it all is this remarkable protein called fibrin – an unsung hero working tirelessly within us to ensure our healthcare needs are met seamlessly.