Enzyme Collection
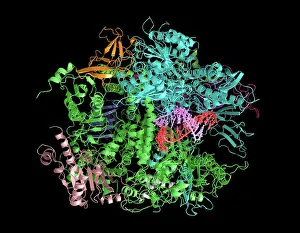
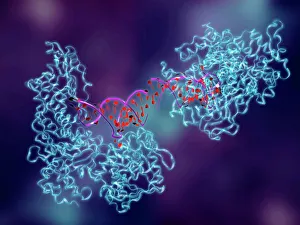
Enzymes: The Molecular Architects of Life DNA transcription, molecular model: they are the key players in the intricate process of DNA transcription
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
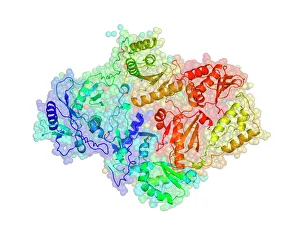
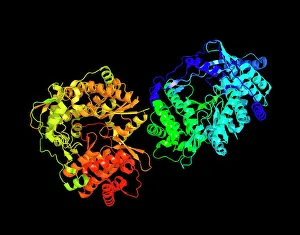
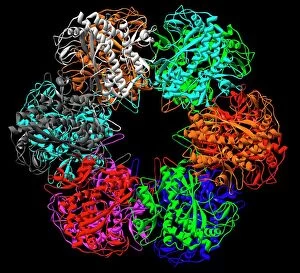
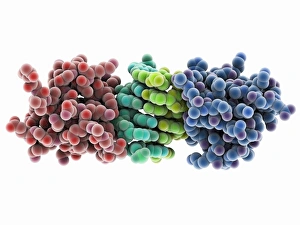
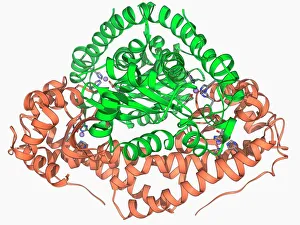
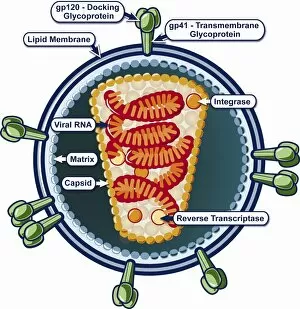
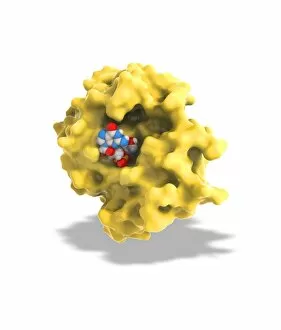
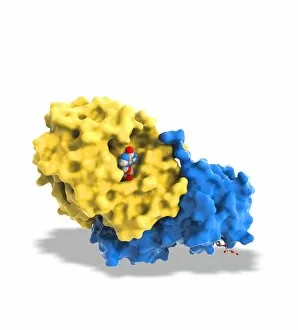
Enzymes: The Molecular Architects of Life DNA transcription, molecular model: they are the key players in the intricate process of DNA transcription, where they faithfully transcribe genetic information into RNA molecules. Metabolic enzyme, artwork: Metabolic enzymes act as catalysts in various biochemical reactions within our bodies, ensuring efficient metabolism and energy production. HIV reverse transcription enzyme: This remarkable enzyme allows the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) to convert its RNA genome into DNA, enabling it to integrate with our own genetic material. Hepatitis C virus enzyme, molecular model: Understanding the structure and function of hepatitis C virus enzymes is crucial for developing effective treatments against this persistent viral infection. Anatomy of Organs Engraving: Enzymes play a vital role in maintaining organ health by facilitating essential processes like digestion, respiration, and hormone regulation throughout our body's intricate anatomy. Manganese superoxide dismutase enzyme F006 / 9423: This antioxidant enzyme protects cells from harmful free radicals by converting them into less damaging substances—a guardian against oxidative stress. Cytochrome b5 molecule C015 / 6696: As an electron carrier protein found in cell membranes, cytochrome b5 assists other enzymes in performing critical metabolic reactions involved in energy production and lipid metabolism. Glutamine synthetase enzyme: Essential for nitrogen metabolism, glutamine synthetase ensures that ammonia produced during cellular processes is safely converted into non-toxic compounds like amino acids or urea. RNA-editing enzyme, molecular model: These specialized enzymes modify RNA molecules after their synthesis—fine-tuning gene expression patterns and expanding the diversity of proteins encoded by our genes. ATPase molecule: ATPases are indispensable for cellular energy transfer; these enzymes hydrolyze adenosine triphosphate (ATP), releasing stored energy to power various cellular processes.