Cytoskeleton Collection (page 3)
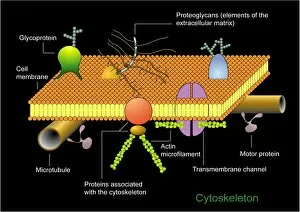
The cytoskeleton, a complex network of protein structures, plays a vital role in maintaining the shape and structure of cells
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
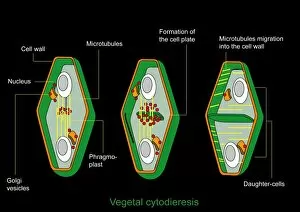
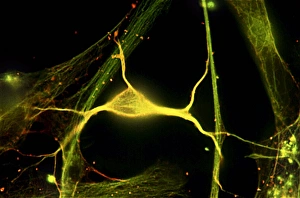
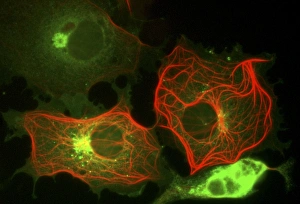
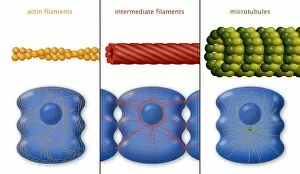
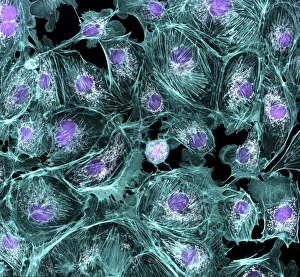
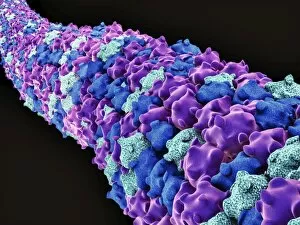
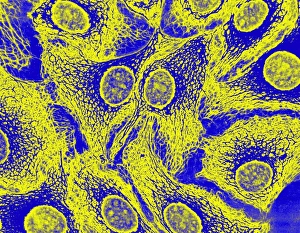
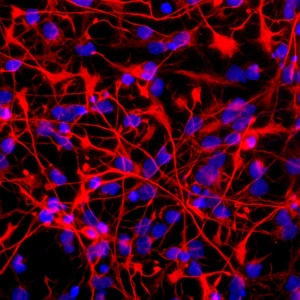
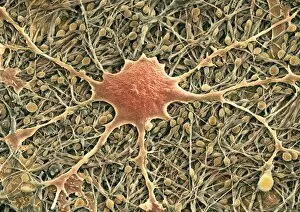
The cytoskeleton, a complex network of protein structures, plays a vital role in maintaining the shape and structure of cells. In budding yeast cells, it ensures proper cell division and growth. Nerve and glial cells rely on the cytoskeleton for their intricate connections, as seen in stunning light micrographs. Glial cells also exhibit their unique structure under confocal light microscopy. HeLa cells, another type of human cell line, reveal the intricate web-like nature of the cytoskeleton when observed through a light microscope. This structural framework supports various cellular processes within HeLa cells. Protozoa, fascinating single-celled organisms that scavenge for particles or absorb nutrients from their environment, also possess a cytoskeletal system to maintain their shape and enable movement. The microscopic view showcases this essential feature. Artwork depicting proteins interacting with microtubules highlights how these components contribute to overall cell function. Microtubules serve as highways for transporting materials within the cell. Conceptual images further illustrate the significance of the cytoskeleton across different organisms. Radiolarians showcase an intricate skeletal frame that provides support and protection while allowing them to move gracefully through water. A conceptual image of a plant cell emphasizes its various components supported by the cytoskeleton. Whether it's shaping budding yeast cells or enabling movement in protozoa or radiolarians, the cytoskeleton is an indispensable component responsible for maintaining cellular architecture and facilitating crucial biological processes across diverse organisms.