Cytoskeletal Collection
"Cytoskeletal Wonders: Exploring the Intricate World of Nerve and Glial Cells" Delving into the fascinating realm of nerve and glial cells
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
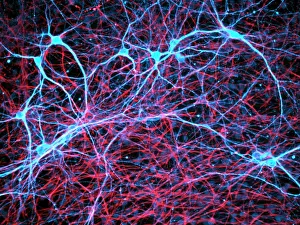
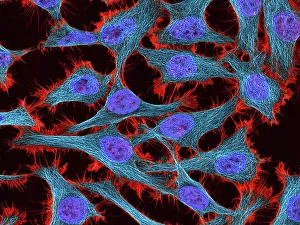
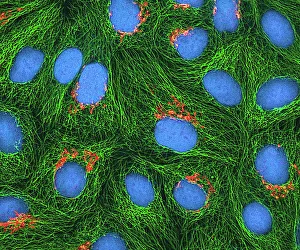
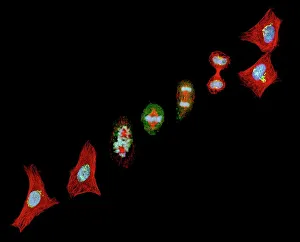
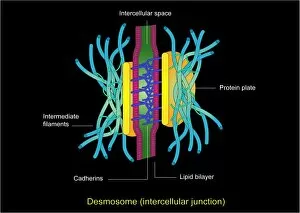
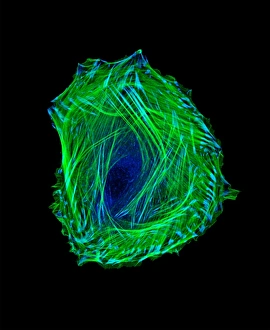
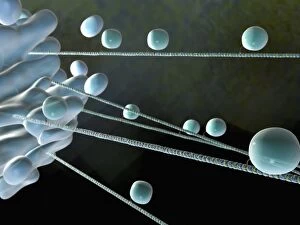
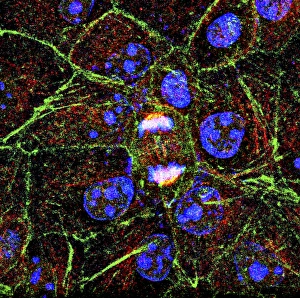
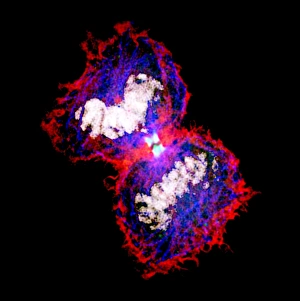
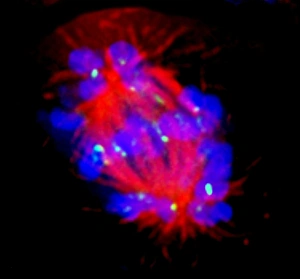
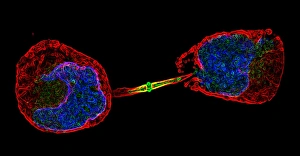
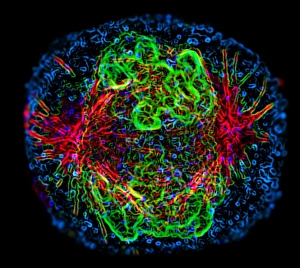
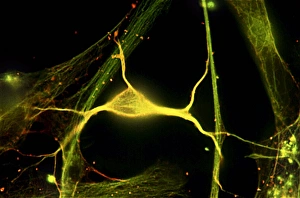
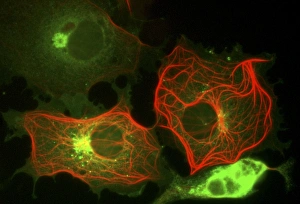
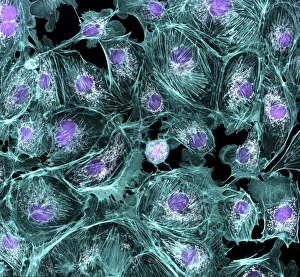
"Cytoskeletal Wonders: Exploring the Intricate World of Nerve and Glial Cells" Delving into the fascinating realm of nerve and glial cells, this light micrograph captures their intricate cytoskeletal structures in stunning detail. Witness the beauty of HeLa cells under a microscope with these captivating light micrographs (C017 / 8299) that unveil the complexity of their cytoskeleton. Unveiling another glimpse into HeLa cells' hidden world, this mesmerizing light micrograph (C017 / 8298) showcases their unique cytoskeletal patterns. Behold the breathtaking process of mitosis through this captivating light micrograph, where every stage is meticulously captured to reveal the dynamic nature of cell division. In an artistic representation, witness how proteins intricately interact with microtubules within a cell's cytoskeleton, forming a complex network crucial for cellular functions. Embark on a visual journey as embryonic smooth muscle cells come to life in this striking image (C018 / 8595), showcasing their well-organized cytoskeletal arrangement. Explore the formation of microtubules within cells through an illuminating illustration (C018 / 0804), shedding light on one aspect dynamics essential for cellular structure and function. Through imaginative artwork (C013 / 5001), delve into the mysterious world of intracellular transport as it navigates along intricate pathways within a cell's bustling interior. Immerse yourself in another artistic depiction (C013 / 4997) that unravels the enigmatic process of intracellular transport, highlighting its significance in maintaining cellular homeostasis and communication. Capturing yet another facet of intracellular transport's complexity, this intriguing artwork (C013 / 4995) unveils how vital molecules navigate through crowded cellular highways to reach their destinations.