Cytosine Collection
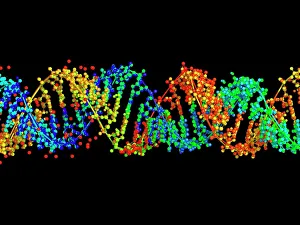
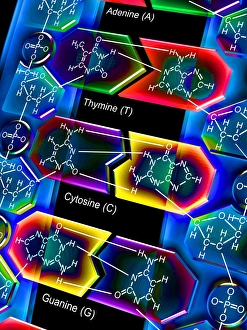
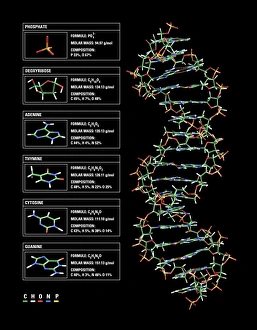
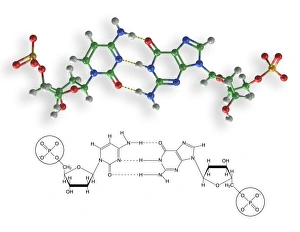
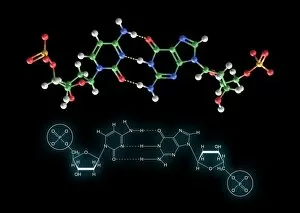
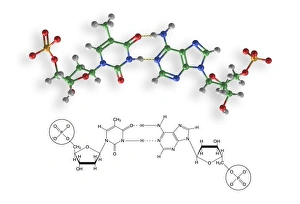
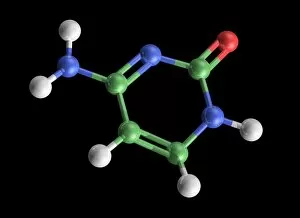
Cytosine, a vital component of the double-stranded RNA molecule and DNA molecule, plays a crucial role in the nucleotide base matrix
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
Cytosine, a vital component of the double-stranded RNA molecule and DNA molecule, plays a crucial role in the nucleotide base matrix. With its distinct structure depicted in artwork resembling intricate DNA molecules, cytosine's significance cannot be overstated. Its presence is essential for various scientific breakthroughs like grapevine genome sequencing, unraveling the secrets hidden within our genetic makeup. As we delve deeper into understanding DNA's complex structure through captivating artwork such as C017 / 7218, cytosine emerges as an integral part of this fundamental building block of life. Conceptual images further emphasize its importance by illustrating the intricate nature of DNA and highlighting cytosine's position within it. These visuals serve as reminders that every strand of DNA contains this remarkable nucleotide base - cytosine - contributing to our existence and offering endless possibilities for scientific exploration.