Cytoplasm Collection
"Cytoplasm: The Dynamic Hub of Cellular Activity" The cytoplasm, a bustling and vibrant region within the cell, plays a crucial role in various cellular processes
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
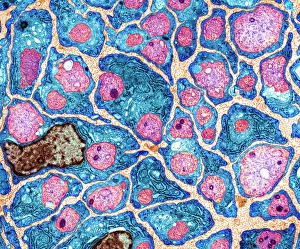
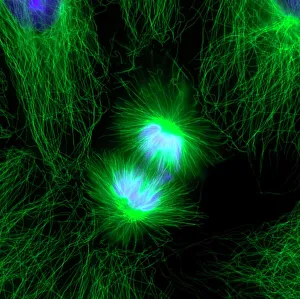
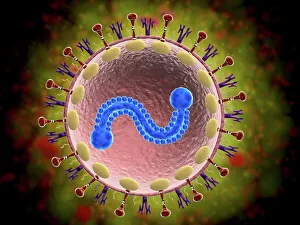
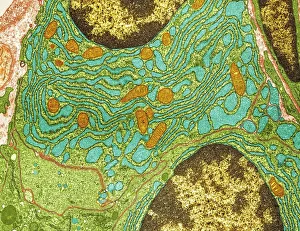
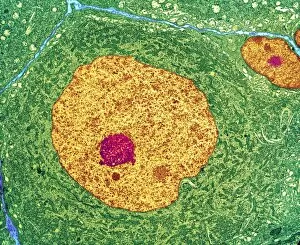
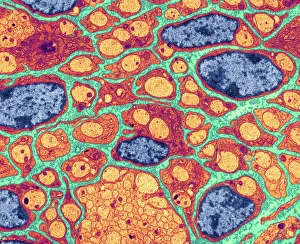
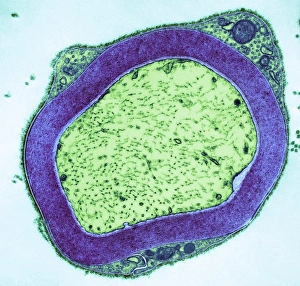
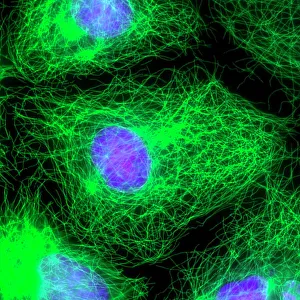
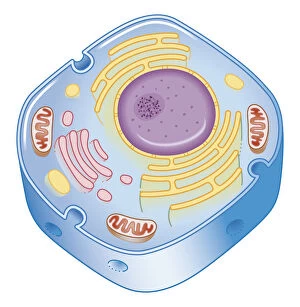
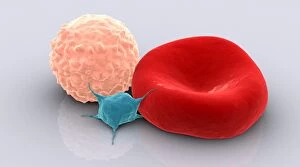
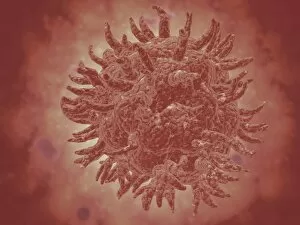
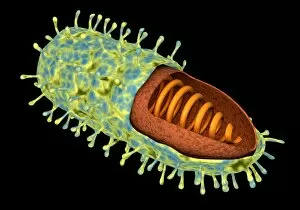
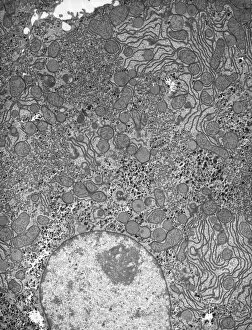
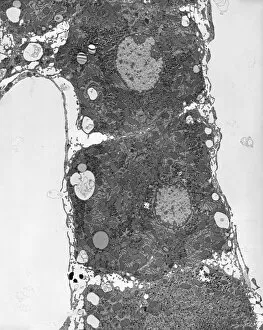
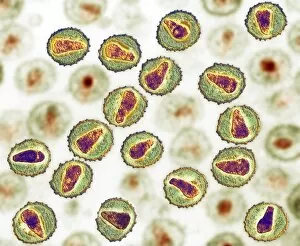
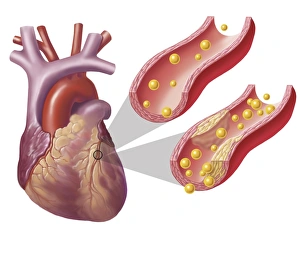
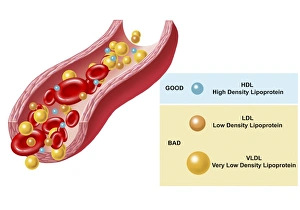
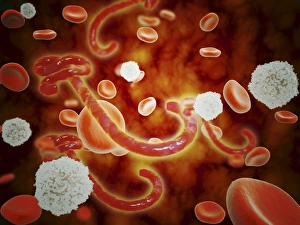
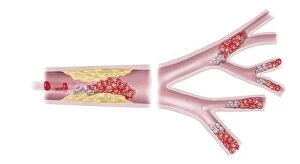
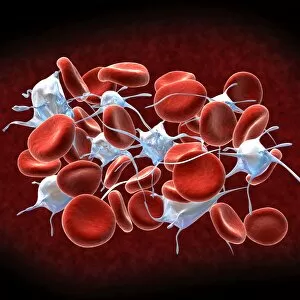
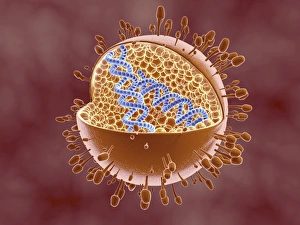
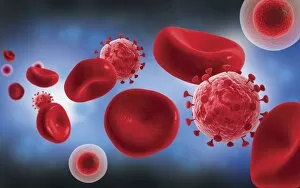
"Cytoplasm: The Dynamic Hub of Cellular Activity" The cytoplasm, a bustling and vibrant region within the cell, plays a crucial role in various cellular processes. Through advanced techniques like Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) and fluorescent micrograph imaging, scientists have unraveled its intricate functions. In nerve cells, myelination of nerve fibers is a remarkable phenomenon that enhances signal transmission. TEM images reveal the mesmerizing beauty of these intricately wrapped fibers, highlighting the importance in maintaining efficient communication within our nervous system. During cell division, another captivating process captured through fluorescent micrographs, the cytoplasm orchestrates an elaborate dance to ensure accurate distribution of genetic material. These stunning visuals showcase how this dynamic organelle actively participates in life's fundamental cycle. Exploring further into TEM imagery unveils plasma cells with their distinctive appearance. Cytoplasmic structures are clearly visible as they produce antibodies vital for immune defense against pathogens such as human respiratory syncytial virus – depicted here under microscopic view. Fascinatingly, not only does cytoplasm support specialized cells but also aids viruses themselves. In AIDS infections visualized by TEM, we witness viral particles budding from host cells' cytoplasms – shedding light on the intricate relationship between pathogen and host. Delving deeper into cellular architecture reveals an illustration showcasing the nucleus containing essential components like mitochondria units, DNA strands coiled into chromosomes – all enveloped within a sea of cytoplasm. This conceptual image emphasizes its pivotal role in preserving genetic information and supporting vital cellular functions. Finally, a captivating artwork depicts platelets alongside red and white blood cells – symbolizing harmony within our circulatory system. The presence of these diverse cell types underscores how each relies on well-coordinated interactions facilitated by the ever-active cytoplasm. Whether it be myelination in nerve fibers or aiding viral replication or participating in cell division, the cytoplasm emerges as a dynamic and indispensable hub of cellular activity.