Copepoda Collection
Copepoda, a diverse group of crustaceans, are found in various aquatic environments ranging from the deep sea to freshwater lakes
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
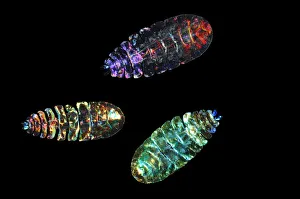
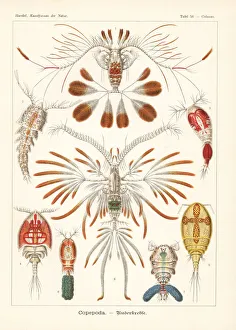
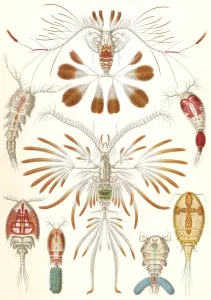
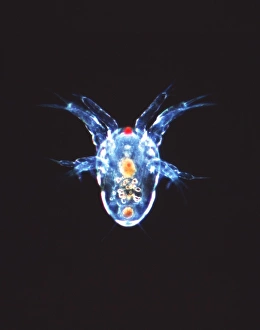
Copepoda, a diverse group of crustaceans, are found in various aquatic environments ranging from the deep sea to freshwater lakes. These tiny creatures play crucial roles in marine ecosystems as both predators and prey. One fascinating example of copepod interaction is seen with the Greenland shark (Somniosus microcephalus) and its parasitic copepod companion, Ommatokoita elongata. This copepod attaches itself to the shark's eyes, feeding on its host's blood and tissue. Despite this seemingly harmful relationship, it does not significantly harm the shark. Marine planktonic copepods like Sapphirina sp. , known for their vibrant colors, are another captivating sight. These small organisms drift along ocean currents, forming an essential part of the marine food chain. Their presence can create mesmerizing displays when illuminated by sunlight or artificial light sources. In scientific research laboratories such as The Natural History Museum in London, dedicated scientists study these remarkable creatures up close. Through careful observation and analysis under light microscopes, they unravel the mysteries surrounding copepod behavior and adaptations. The intricate world also includes various species that act as parasites on other organisms. These parasites have evolved unique mechanisms to attach themselves to their hosts while extracting nutrients for survival. Illustrations showcasing different types of copopod crustaceans highlight their incredible diversity within the Copepoda class. From calanoid planktonic copepods to those with distinct physical features or behaviors - each species contributes uniquely to our understanding of this complex group.