Clepsydra Collection
The clepsydra, also known as the water clock, is an ancient timekeeping device that dates back to 270 BC
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
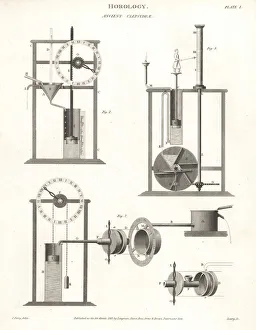
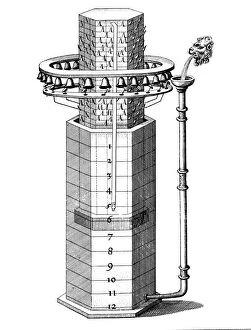
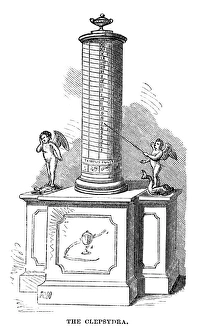
The clepsydra, also known as the water clock, is an ancient timekeeping device that dates back to 270 BC. Invented by Ctesibius of Alexandria, this remarkable invention revolutionized the way people measured time in the past. One can only imagine the ingenuity and craftsmanship required to construct a clepsydra during those times. A reconstruction of this incredible device from 1857 showcases its intricate design and mechanism. The image captures the essence of an era where innovation was at its peak. Water clocks or clepsydrae continued to evolve throughout history, as depicted in an illustration from Les Raisons des Forces Mouvantes. This chromolitho artwork beautifully portrays a water clock's elegance and sophistication during the 18th century. An old engraving further emphasizes how these ancient clepsydras were meticulously crafted with precision and attention to detail. The black-and-white photo transports us back in time, allowing us to appreciate their timeless beauty. One particular water clock from 1617-1619 stands out for not only indicating hours but also chiming melodiously. Imagine living in a world where your day was marked by such enchanting sounds emanating from this marvelous contraption. The Tower of Winds in Athens, Greece serves as a testament to how integral water clocks were in ancient civilizations' daily lives. Its presence reminds us of their significance beyond mere timekeeping - they represented cultural progress and scientific advancement. Clepsydra Geyser erupting into the air under grey clouds at Yellowstone National Park evokes awe-inspiring natural wonders intertwined with human-made inventions like water clocks. It symbolizes our eternal fascination with measuring time amidst nature's grandeur. Even today, we marvel at these ingenious creations through illustrations like one found in Abraham Rees' Cyclopaedia Or Universal Dictionary Of Arts, Sciences And Literature published in London (1820). This depiction highlights how far-reaching their influence was, transcending borders and time.