Claudius Ptolemy Collection
Claudius Ptolemy, a renowned astronomer and geographer of ancient times, left an indelible mark on the world with his groundbreaking work
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
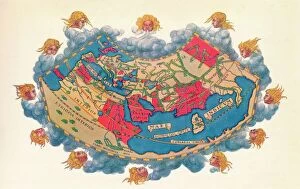
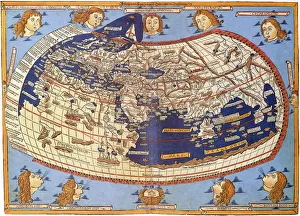
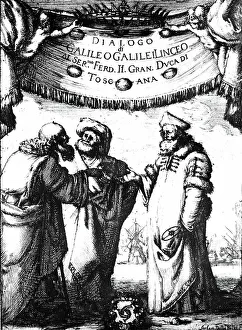
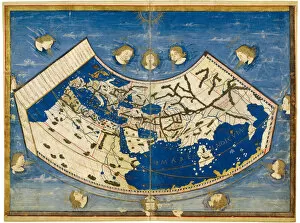
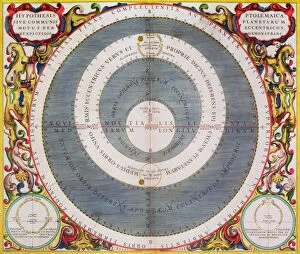
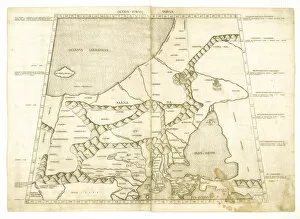
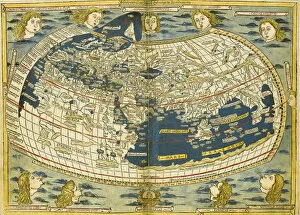
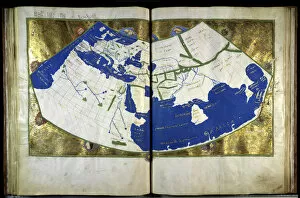
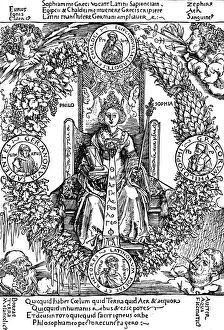
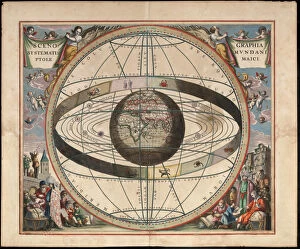
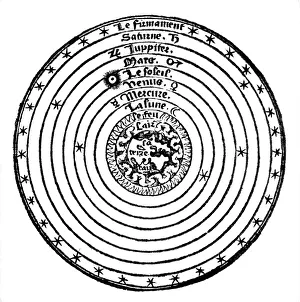
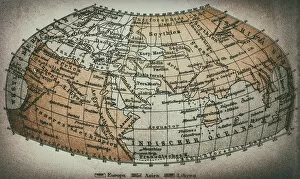
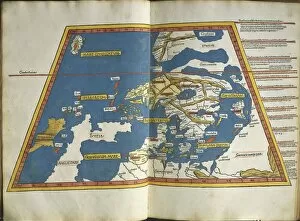
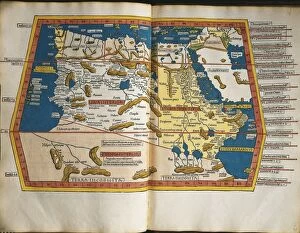
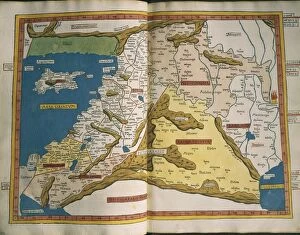
Claudius Ptolemy, a renowned astronomer and geographer of ancient times, left an indelible mark on the world with his groundbreaking work. His most notable contribution was the creation of Ptolemy's Map of the World in AD 150, which depicted the known world at that time. This map served as a foundation for cartography for centuries to come. Ptolemy's World map from 1467 is a testament to his meticulous research and dedication to accuracy. It showcased not only geographical features but also celestial bodies, demonstrating his deep understanding of astronomy. His maps were highly influential and widely used during the Renaissance period. Galileo Galilei, another brilliant mind in scientific history, paid homage to Ptolemy by featuring his work prominently in Dialogo sopra i due massimi sistemi del mondo published in 1632. The frontispiece engravings beautifully captured Ptolemy's contributions alongside other astronomers who shaped our understanding of the universe. The triumph of Truth, depicted in stunning oil paintings from the 19th century, further immortalized Claudius Ptolemy and his fellow astronomers. These artworks portrayed their significant role in unraveling universal truths through observation and analysis. One such engraving dedicated solely to Claudius Ptolemy showcases him as an esteemed figure deserving recognition for revolutionizing geography and astronomy alike. His legacy lives on through these artistic representations that celebrate his intellectual prowess. Additionally, Borso d'Este's Atlas created around 1466-1467 featured works by Germanus Nicolaus Donnus—a testament to how far-reaching Ptolemy's influence was even beyond his own lifetime. Claudius Ptolemy remains an icon among scholars throughout history due to his pioneering efforts in mapping out our world both physically and celestially. His enduring impact continues to shape modern science while inspiring future generations of explorers and thinkers.