Cell Nucleus Collection
The cell nucleus, often referred to as the control center of a plant cell, holds a world of mysteries waiting to be unraveled
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
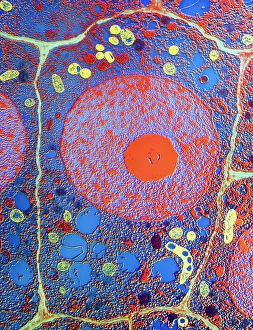
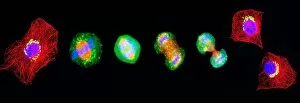
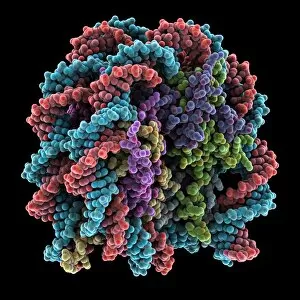
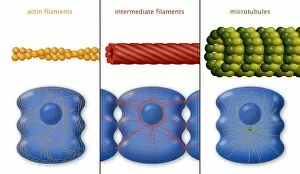
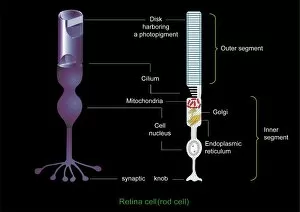
The cell nucleus, often referred to as the control center of a plant cell, holds a world of mysteries waiting to be unraveled. In this captivating multiphoton fluorescence image of HeLa cells, we catch a glimpse into the intricate beauty that lies within. The nucleus stands out amidst the bustling activity with its distinct structure and importance. Just like in skin anatomy artwork, where every layer plays a crucial role in maintaining our body's integrity, the nucleus acts as the guardian of genetic information. It orchestrates vital processes through its various components and interactions. Take for instance the cytoskeleton in unicellular parasites captured under SEM C018 / 0518 - it showcases how even these tiny organisms rely on their nuclei for survival. Genetic metaphase analysis provides us with invaluable insights into cellular division and DNA replication. As seen in images C019 / 0289 and C019 / 0288, chromosomes align meticulously during metaphase ensuring accurate distribution of genetic material to daughter cells. Eukaryotic cell nucleus artwork further emphasizes its significance by highlighting its complex architecture and functions. Within this hub of activity lies chromatin remodelling factors diligently working alongside DNA (C015 / 5156 & C015 / 5155). Together they sculpt gene expression patterns essential for development and adaptation. But how does information enter or exit this central command? Importin protein complexes play an integral role here as depicted in images C015 / 5149 & C015 / 5148 where they are seen interacting with enzymes at nuclear pores. These gatekeepers ensure only authorized molecules gain access while safeguarding against potential threats. Intriguingly, human chromosomes magnified under SEM remind us that each individual possesses their own unique blueprint stored within their nuclei. This microscopic universe encapsulates our identity and hereditary traits passed down through generations. As we delve deeper into understanding the wonders held within each cell nucleus, we unlock secrets that could revolutionize medicine, agriculture, and beyond.