Body Temperature Collection
"Exploring the Intricacies of Body Temperature: From Thermograms to Digital Readings" Taking temperature is a vital part of monitoring our health and well-being
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
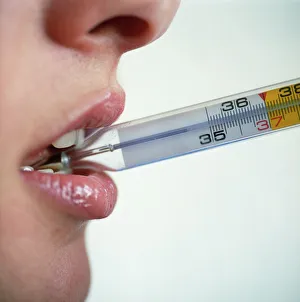
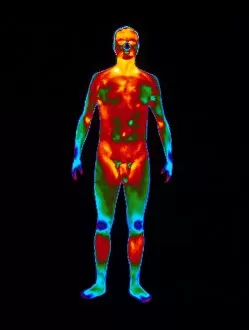
"Exploring the Intricacies of Body Temperature: From Thermograms to Digital Readings" Taking temperature is a vital part of monitoring our health and well-being. Whether it's through traditional methods or modern technology, understanding body temperature helps us stay in tune with our bodies. A thermogram captures an intriguing image of a standing naked man from the front view, showcasing the distribution of heat across his body. This visual representation allows us to observe variations in temperature and identify potential areas of concern. In contrast, a digital thermometer displays a fever reading (C014 / 0109), indicating an elevated body temperature. This essential tool provides accurate measurements within seconds, aiding in early detection and prompt medical attention if necessary. Artwork depicting breathing and body temperature (C013 / 5938) highlights the intimate connection between respiration and thermal regulation. Our breaths can influence our internal thermostat, reminding us how interconnected these bodily functions truly are. Nature also offers fascinating thermal adaptation. The marine iguana, for instance, adjusts its body temperature according to its surroundings—an incredible feat that showcases nature's adaptability. Thermograms further demonstrate this concept by capturing images of babies' bodies at different temperatures. These snapshots reveal their ability to regulate their internal warmth effectively as they grow and develop. From infancy to adulthood, thermograms continue to provide valuable insights into human physiology. Another striking image portrays a standing naked man from the front view—a reminder that each individual possesses unique patterns when it comes to maintaining optimal body heat levels. Ultimately, whether we're examining infants or adults through thermography or relying on digital thermometers for quick readings—body temperature remains an essential aspect of our overall health management journey. Understanding these intricacies empowers us to take proactive measures towards maintaining balance within ourselves.