Atoms Collection (page 8)
"Unveiling the Mysteries of Atoms: From Northern Lights to Quantum Marvels" Witness the captivating dance under the shimmering Northern lights
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
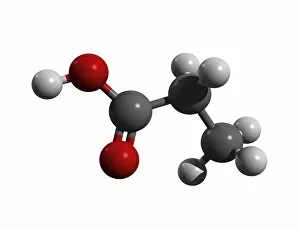
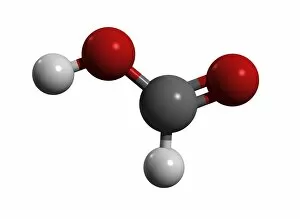
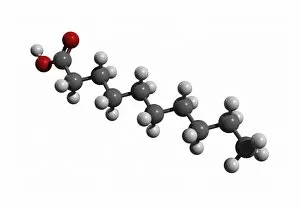
"Unveiling the Mysteries of Atoms: From Northern Lights to Quantum Marvels" Witness the captivating dance under the shimmering Northern lights, a celestial spectacle that mirrors their intricate nature. Niels Bohr, a pioneer in atomic theory, immortalized through a whimsical caricature capturing his profound contributions to our understanding of atoms. Behold the explosive beauty of nuclear fission artwork, showcasing the immense power harnessed within tiny atomic nuclei. Delve into the microscopic world as we explore HIV reverse transcription enzyme—a remarkable atom-driven process crucial for viral replication. Ernest Rutherford's genius encapsulated in an amusing caricature, symbolizing his groundbreaking experiments that unraveled atomic structure. Embark on an artistic journey depicting the evolution of our universe—where atoms play a pivotal role in shaping cosmic wonders beyond imagination. Witness the exhilarating collision between particles—an awe-inspiring event revealing hidden secrets about matter and energy at its most fundamental level. Step into a simulated realm where Bose-Einstein condensate defies conventional physics—unleashing mind-bending phenomena like superfluidity and quantum coherence. Discover oxytocin—the enchanting neurotransmitter molecule responsible for bonding and affection, reminding us how atoms shape human emotions and connections. Explore density within a Bose-Einstein condensate—a surreal state where atoms merge into one entity with extraordinary properties yet to be fully understood by science. Bonus: Dive into "When The Atoms Failed, " an intriguing cover story from Amazing Stories Scifi magazine—transporting readers to alternate realities shaped by unexpected atomic anomalies. Witness nature's own masterpiece as Aurora Borealis illuminates a snowy coniferous forest in Northern Finland—a breathtaking reminder of how atoms interact with Earth's magnetic field to create this ethereal phenomenon during March nights.