Atmospheric Pressure Collection
Atmospheric pressure, a force that surrounds us all, has fascinated scientists for centuries
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
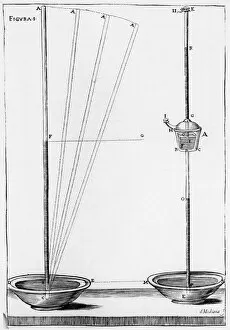
Atmospheric pressure, a force that surrounds us all, has fascinated scientists for centuries. In the year 1851, an exploration into this intriguing phenomenon began with the study of equilibrium and movement of the air. This research was further enhanced by the invention of the barometer in 1936 by Max Fernekes. The field barometer, depicted in a vibrant chromolitho image, became an essential tool for measuring atmospheric pressure. An annotated illustration showcased various types of barometers including pendent, diagonal, and marine ones. These engravings provided valuable insights into their mechanisms. Evangelista Torricelli, an Italian physicist and mathematician renowned for his contributions to fluid mechanics and vacuum physics, played a significant role in understanding atmospheric pressure. His famous demonstration involving a column of liquid unveiled the effect of this force on our surroundings. In another captivating chromolitho depiction from 1873, we witness Torricelli inventing the mercury barometer back in 1643. This groundbreaking invention revolutionized our ability to measure atmospheric pressure accurately. Not limited to mercury-based devices alone, Von Guerickes' water barometer from 1672 demonstrated alternative methods for gauging this invisible force surrounding us. Blaise Pascal's contribution as a French mathematician and physicist cannot be overlooked either; his work greatly influenced our understanding during the 17th century. The Accademia dell Cimento in Florence utilized experimental barometers in their quest to unravel nature's secrets around 1691. These instruments served as vital tools aiding their scientific investigations. Through these historical artifacts and illustrations spanning several centuries, we gain insight into humanity's relentless pursuit to comprehend atmospheric pressure—a fundamental aspect shaping our environment since time immemorial.