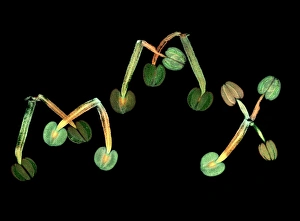Arabidopsis Thaliana Collection
Arabidopsis thaliana, commonly known as Thale cress or mouse-ear cress, is a small flowering plant that has captivated scientists and researchers worldwide
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
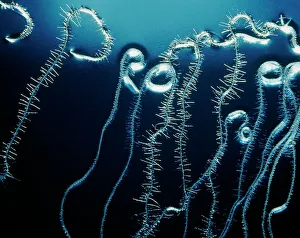
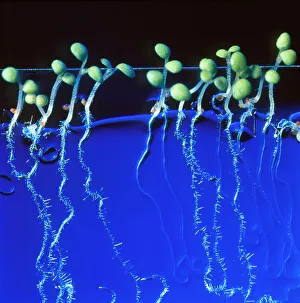
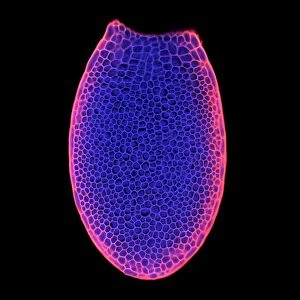
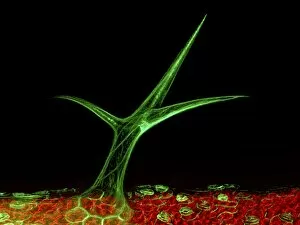
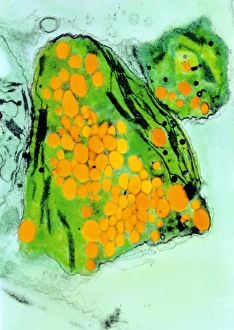
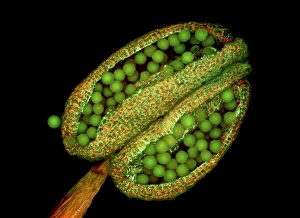
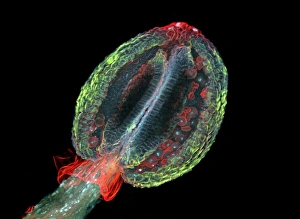
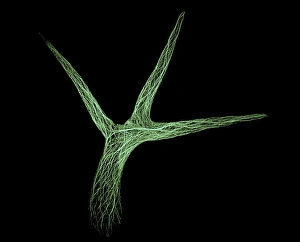
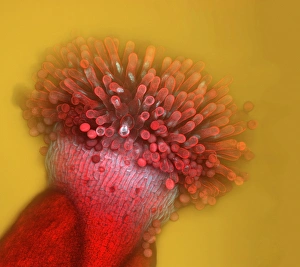
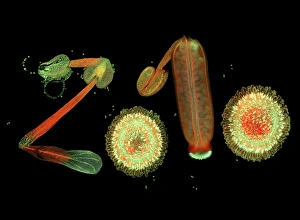
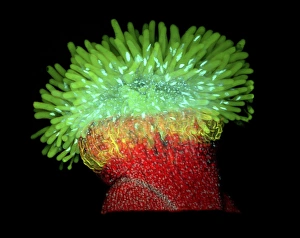
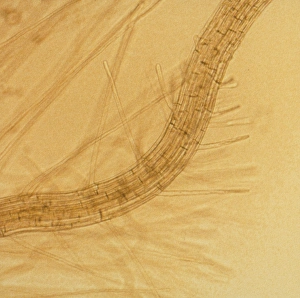
Arabidopsis thaliana, commonly known as Thale cress or mouse-ear cress, is a small flowering plant that has captivated scientists and researchers worldwide. Its intricate root system serves as the foundation for its growth and survival. In laboratories around the globe, this cultured cress plant has become an invaluable tool in studying various aspects of plant biology. From understanding the role of plant hormones to unraveling the mysteries of embryonic development, it offers endless possibilities. The delicate beauty of its flowers can be seen under a microscope through stunning micrographs. These images reveal the intricate details of Thale cress flower petals, captivating scientists with their mesmerizing patterns. Also referred to by different names like Arabis thaliana and Arabette rameuse, this remarkable plant species continues to amaze researchers with its versatility. Molecular models showcasing plant hormone regulators provide insights into how these tiny molecules orchestrate complex biological processes within Arabidopsis thaliana. Examining Thale cress leaf stomata through scanning electron microscopy reveals fascinating structures responsible for gas exchange in plants. These SEM images offer glimpses into nature's intricacy at a microscopic level. Illustrations depicting Thale cress showcase its unique characteristics and serve as visual aids in scientific studies. Through detailed drawings, researchers gain a deeper understanding of this extraordinary organism's anatomy and morphology. Micrographs capturing Arabidopsis thaliana embryos unveil the early stages of life within this resilient species. The study of these embryos provides crucial insights into developmental biology and genetic mechanisms governing growth and reproduction. Beyond scientific research, it also plays a vital role in exploring plant odour research. By investigating scent production in this humble herbaceous model organism, scientists hope to unlock secrets about communication between plants and their environment. Thale cress anthers brimming with pollen grains illustrate yet another fascinating aspect of this versatile species' reproductive system.